 |
|
Tel:+86-022-58602231
 |
|
| CasNo: | 474-25-9 |
|---|---|
| ProductName: |
Chenodeoxycholic Acid |
| MolecularFormula: | C24H40O4 |
| Appearance: | White crystalline powder |
| Price: | Negotiable |
| ProductionCapacity: | 3 ton/month |
| Inquiry |
What Is Chenodeoxycholic acid?
Chenodeoxycholic acid (also known as chenodesoxycholic acid, chenocholic acid and 3α,7α-dihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid) is a bile acid. It occurs as a white crystalline substance insoluble in water but soluble in alcohol and acetic acid, with melting point at 165-167 °C. Salts of this carboxylic acid are called chenodeoxycholates. Chenodeoxycholic acid is one of the main bile acids produced by the liver.
It was first isolated from the bile of the domestic goose, which gives it the "cheno" portion of its name (Greek: χ?ν = goose).
Chenodeoxycholic acid and cholic acid are the two primary bile acids in humans. Some other mammals have muricholic acid or deoxycholic acid rather than chenodeoxycholic acid.
Chenodeoxycholic acid is synthesized in the liver from cholesterol by a process which involves several enzymatic steps. Like other bile acids, it can be conjugated in the liver with taurine or glycine, forming taurochenodeoxycholate or glycochenodeoxycholate. Conjugation results in a lower pKa. This means the conjugated bile acids are ionized at the usual pH in the intestine and will stay in the gastrointestinal tract until reaching the ileum where most will be reabsorbed. Bile acids form micelles which facilitate lipid digestion. After absorption, they are taken up by the liver and resecreted, so undergoing an enterohepatic circulation. Unabsorbed chenodeoxycholic acid can be metabolised by bacteria in the colon to form the secondary bile acid known as lithocholic acid.
Choendeoxycholic acid is the most potent natural bile acid at stimulating the nuclear bile acid receptor, farnesoid X receptor (FXR). The transcription of many genes is activated by FXR.
Chenodeoxycholic acid Therapeutic applications
Chenodeoxycholic acid has been used as medical therapy to dissolve gallstones.
Chenodeoxycholic acid can be used in the treatment of cerebrotendineous xanthomatosis.
The Australian biotechnology company Giaconda has tested a treatment for Hepatitis C infection that combines chenodeoxycholic acid with bezafibrate.
As diarrhea is a complication of chenodeoxycholic acid therapy, it has also been used to treat constipation.
In supramolecular chemistry, molecular tweezers based on a chenodeoxycholic acid scaffold is a urea receptor that can contain anions in its binding pocket in order of affinity: H2PO4? (dihydrogen phosphate) > Cl? > Br? > I? reflecting their basicities (tetrabutylammonium counter ion).
Chenodeoxycholic acid is made from bile acid, a substance that occurs naturally in the body.
Chenodeoxycholic acid is used to dissolve gallstones in people who cannot have gallbladder surgery.
Chenodeoxycholic acid may also be used for purposes not listed in this medication guide.
Chenodeoxycholic acid can harm an unborn baby or cause birth defects. Do not use if you are pregnant.
You should not use Chenodeoxycholic acid if you are allergic to it, or if you have liver disease, cirrhosis, or certain conditions that cause an obstruction in your digestive system.
Before you take Chenodeoxycholic acid, tell your doctor if you have a history of liver problems or jaundice.
While using Chenodeoxycholic acid, you will need frequent medical tests at your doctor's office. Visit your doctor regularly.
Chenodeoxycholic acid is only part of a complete program of treatment that may also include weight control and a special diet. Follow the diet plan created for you by your doctor or nutrition counselor.
Use Chenodeoxycholic acid regularly to get the most benefit. It may take up to 12 months before your symptoms improve. Chenodeoxycholic acid is usually given for no longer than 2 years.
Even with treatment, there is a chance that your gallstones may return within 5 years. Chenodeoxycholic acid will not prevent gallstones from occurring.
You should not use Chenodeoxycholic acid if you are allergic to it, if you are pregnant, or if you have liver disease, cirrhosis, or certain conditions that cause an obstruction in your digestive system.
To make sure you can safely use Chenodeoxycholic acid, tell your doctor if you have a history of liver problems or jaundice.
'FDA pregnancy category X. This medication can harm an unborn baby or cause birth defects. Do not use chenodiol if you are pregnant. Tell your doctor right away if you become pregnant during treatment. Use effective birth control while you are using this medication.
It is not known whether Chenodeoxycholic acid passes into breast milk or if it could harm a nursing baby. Do not use this medication without telling your doctor if you are breast-feeding a baby.
Chenodeoxycholic Acid Chemistry
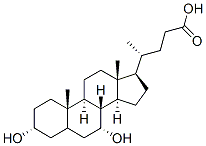
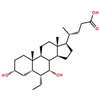
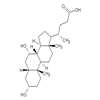
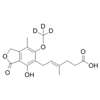
Structure of Chenodeoxycholic acid (CAS NO.474-25-9):
IUPAC Name: (4R)-4-[(3R,5S,7R,8R,9S,10S,13R,14S,17R)-3,7-dihydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-2,
3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pentanoic acid
Empirical Formula: C24H40O4
Molecular Weight: 392.572
EINECS: 207-481-8
Index of Refraction: 1.543
Molar Refractivity: 109.65 cm3
Molar Volume: 347.8 cm3
Polarizability: 43.46×10-24cm3
Surface Tension: 46 dyne/cm
Density: 1.128 g/cm3
Flash Point: 298.8 °C
Enthalpy of Vaporization: 95.01 kJ/mol
Melting Point: 165-167 °C(lit.)
Boiling Point: 547.1 °C at 760 mmHg
Vapour Pressure: 2.98E-14 mmHg at 25°C
Water Solubility: PRACTICALLY INSOLUBLE
Physical Appearance: Off-White Solid
Product Categories: Intermediates & Fine Chemicals;Pharmaceuticals;Steroids;Intracellular receptor
Chenodeoxycholic Acid Uses
A major bile acid in many vertebrates, occurring as the N-glycine and/or N-taurine conjugate. With other bile acids, forms mixed micelles with lecithin in bile which solubilize cholesterol and thus facilitates its excretion.
Chenodeoxycholic Acid Toxicity Data With Reference
1.
mmo-sat 20 mg/L
MUREAV Mutation Research. 158 (1985),45.
2.
sln-smc 100 mg/L
CRNGDP Carcinogenesis. 5 (1984),447.
3.
orl-wmn TDLo:24 g/kg/5Y-C:CAR
CLONEA Clinics in Oncology. 7 (1981),245.
4.
orl-rat LD50:4000 mg/kg
IYKEDH Iyakuhin Kenkyu. Study of Medical Supplies. 13 (1982),1128.
5.
ipr-rat LD50:105 mg/kg
OYYAA2 Oyo Yakuri. Pharmacometrics. 15 (1978),915.
6.
ivn-rat LD50:106 mg/kg
OYYAA2 Oyo Yakuri. Pharmacometrics. 15 (1978),915.
7.
orl-mus LD50:3000 mg/kg
IYKEDH Iyakuhin Kenkyu. Study of Medical Supplies. 13 (1982),1128.
8.
ipr-mus LD50:86 mg/kg
OYYAA2 Oyo Yakuri. Pharmacometrics. 15 (1978),915.
9.
ivn-mus LD50:100 mg/kg
ARZNAD Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. 20 (1970),323.
Chenodeoxycholic Acid Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by ingestion. An experimental teratogen. Experimental reproductive effects. Questionable human carcinogen producing liver tumors. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and fumes.
Hazard Codes: HarmfulXn
Risk Statements: 63
R63:Possible risk of harm to the unborn child.
Safety Statements: 22-24/25-45-36/37
S22:Do not breathe dust.
S24/25:Avoid contact with skin and eyes.
S45:In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show the label whenever possible.)
S36/37:Wear suitable protective clothing and gloves.
WGK Germany: 2
RTECS: FZ1980000
Accession Number:DB06777
Type: Small Molecule
Groups:Approved
Weight:Average: 392.572
Monoisotopic: 392.292659768
Molecular Framework:Aliphatic homopolycyclic compounds
Chenodeoxycholic acid Substituents
Dihydroxy bile acid, alcohol, or derivatives
7-hydroxysteroid
3-alpha-hydroxysteroid
Hydroxysteroid
3-hydroxysteroid
Cyclic alcohol
Secondary alcohol
Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
Carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acid derivative
Hydrocarbon derivative
Organooxygen compound
Carbonyl group
Alcohol
Aliphatic homopolycyclic compound
Chenodeoxycholic acid Pharmacology
Indication
Chenodiol is indicated for patients with radiolucent stones in well-opacifying gallbladders, in whom selective surgery would be undertaken except for the presence of increased surgical risk due to systemic disease or age. Chenodiol will not dissolve calcified (radiopaque) or radiolucent bile pigment stones.
Pharmacodynamics It acts by reducing levels of cholesterol in the bile, helping gallstones that are made predominantly of cholesterol to dissolve. Chenodeoxycholic acid is ineffective with stones of a high calcium or bile acid content.
Mechanism of action
Chenodiol suppresses hepatic synthesis of both cholesterol and cholic acid, gradually replacing the latter and its metabolite, deoxycholic acid in an expanded bile acid pool. These actions contribute to biliary cholesterol desaturation and gradual dissolution of radiolucent cholesterol gallstones in the presence of a gall-bladder visualized by oral cholecystography. Bile acids may also bind the the bile acid receptor (FXR) which regulates the synthesis and transport of bile acids.
Absorption Chenodiol is well absorbed from the small intestine.
Metabolism
Chenodiol is well absorbed from the small intestine and taken up by the liver where it is converted to its taurine and glycine conjugates and secreted in bile. At steady-state, an amount of chenodiol near the daily dose escapes to the colon and is converted by bacterial action to lithocholic acid. About 80% of the lithocholate is excreted in the feces; the remainder is absorbed and converted in the liver to its poorly absorbed sulfolithocholyl conjugates. During chenodiol therapy there is only a minor increase in biliary lithocholate, while fecal bile acids are increased three- to fourfold.
Route of elimination
About 80% of its bacterial metabolite lithocholate is excreted in the feces.
Chenodeoxycholic Acid Specification
Chenodeoxycholic acid , its cas register number is 474-25-9. It also can be called 3-alpha,7-alpha-Dihydroxy-5-beta-cholan-24-oic acid ; 3-alpha,7-alpha-Dihydroxycholanic acid ; 3-alpha,7-alpha-Dihydroxycholansaeure ; 3alpha,7alpha-Dihydroxy-5beta-cholan-24-oic acid ; 7-alpha-Hydroxylithocholic acid ; Acide chenodeoxycholique ; Acido chenodeoxicholico ; Anthropodeoxycholic acid ; Anthropododesoxycholic acid ; Chenic acid ; Chenix ;
Chenodesoxycholsaeure ; Chenodiol ; Gallodesoxycholic acid .
Chenodeoxycholic acid Side Effects
Commonly reported side effects of chenodeoxycholic acid include increased serum alanine aminotransferase. See below for a comprehensive list of adverse effects.
For the Consumer
Applies to chenodeoxycholic acid: oral tablet
In addition to its needed effects, some unwanted effects may be caused by chenodeoxycholic acid. In the event that any of these side effects do occur, they may require medical attention.
You should check with your doctor immediately if any of these side effects occur when taking chenodeoxycholic acid:
Incidence not known
Black, tarry stools
chest pain
chills
cough
fever
painful or difficult urination
shortness of breath
sore throat
sores, ulcers, or white spots on the lips or in the mouth
swollen glands
unusual bleeding or bruising
unusual tiredness or weakness
Some of the side effects that can occur with chenodeoxycholic acid may not need medical attention. As your body adjusts to the medicine during treatment these side effects may go away. Your health care professional may also be able to tell you about ways to reduce or prevent some of these side effects. If any of the following side effects continue, are bothersome or if you have any questions about them, check with your health care professional:
More common
Diarrhea
Less common
Abdominal or stomach pain
acid or sour stomach
belching
bloated
cramps
difficulty having a bowel movement (stool)
excess air or gas in the stomach or intestines
full feeling
heartburn
indigestion
loss of appetite
nausea and vomiting
pain in the chest below the breastbone
pain or discomfort in chest, upper stomach, or throat
passing gas
stomach discomfort or upset
weight loss
For Healthcare Professionals
Applies to chenodeoxycholic acid: oral tablet
chenodeoxycholic acid Hepatic
Hepatic side effects have included dose-related serum aminotransferase (mainly SGPT) elevations, usually not accompanied by
rises in alkaline phosphatase or bilirubin, occurring in 30% or more of patients treated with the recommended dose of chenodeoxycholic acid. In most cases, these elevations were minor (1? to 3 times the upper limit of laboratory normal) and
transient, returning to within the normal range within six months despite continued administration of the drug.
Morphologic studies of liver biopsies taken before and after 9 and 24 months of treatment with chenodeoxycholic acid have shown that 63% of the patients prior to chenodiol treatment had evidence of intrahepatic cholestasis. Almost all pretreatment patients had electron microscopic abnormalities. By the ninth month of treatment, reexamination of two-thirds of the patients showed an 89% incidence of the signs of intrahepatic cholestasis. Two of 89 patients at the ninth month had lithocholate-like lesions in the canalicular membrane, although there were not clinical enzyme abnormalities in the face of continued treatment and no change in Type 2 light microscopic parameters.[Ref]
chenodeoxycholic acid Gastrointestinal
Gastrointestinal side effects have included diarrhea in 30% to 40% of patients and may occur at any time during treatment, but is most commonly encountered when treatment is initiated. Usually, the diarrhea is mild, translucent, well-tolerated and does not
interfere with therapy. Other less frequent, gastrointestinal side effects reported include urgency, cramps, heartburn, constipation, nausea and vomiting, anorexia, epigastric distress, dyspepsia, flatulence and nonspecific abdominal pain.
chenodeoxycholic acid Hematologic
Hematologic side effects have included decreases in white cell count but the drug was continued in all patients without incident.
chenodeoxycholic acid Metabolic
Metabolic side effects have included serum total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol increases of 10% or more during drug administration; no change has been seen in the high-density lipoprotein (HDL) fraction; small decreases in serum triglyceride levels for females have been reported.
Chenodeoxycholic Acid Keyword
chenodeoxycholic acid
chenodeoxycholic acid brand name
chenodeoxycholic acid synthesis
chenodeoxycholic acid tablets
chenodeoxycholic acid gallstones
chenodeoxycholic acid 中文
Chenodeoxycholic Acid for sale
Chenodeoxycholic Acid uses
where to buy Chenodeoxycholic Acid
buy Chenodeoxycholic Acid
where can i buy Chenodeoxycholic Acid
where to get Chenodeoxycholic Acid
Chenodeoxycholic Acid where to buy
Chenodeoxycholic Acid safety
Chenodeoxycholic Acid buy
where can you buy Chenodeoxycholic Acid
where can i get Chenodeoxycholic Acid
can you buy Chenodeoxycholic Acid
Chenodeoxycholic Acid storage
Chenodeoxycholic Acid formula
Chenodeoxycholic Acid purchase
Chenodeoxycholic Acid manufacturers
buy Chenodeoxycholic Acid online
Chenodeoxycholic Acid sale
formula for Chenodeoxycholic Acid
purchase Chenodeoxycholic Acid
Chenodeoxycholic Acid buy online
Chenodeoxycholic Acid suppliers
how to make Chenodeoxycholic Acid
formula Chenodeoxycholic Acid
Chenodeoxycholic Acid cas
uses of Chenodeoxycholic Acid
what is Chenodeoxycholic Acid
what is Chenodeoxycholic Acid used for
write the formula for Chenodeoxycholic Acid
how to buy Chenodeoxycholic Acid
how to get Chenodeoxycholic Acid
msds Chenodeoxycholic Acid
the formula for Chenodeoxycholic Acid
Chenodeoxycholic Acid formula name
uses for Chenodeoxycholic Acid
Chenodeoxycholic Acid chemical formula
chemical formula for Chenodeoxycholic Acid
what is the formula for Chenodeoxycholic Acid
msds for Chenodeoxycholic Acid
use of Chenodeoxycholic Acid
formula of Chenodeoxycholic Acid
msds of Chenodeoxycholic Acid
chemical formula of Chenodeoxycholic Acid
what is the chemical formula for Chenodeoxycholic Acid
how to store Chenodeoxycholic Acid
storing Chenodeoxycholic Acid
how to make Chenodeoxycholic Acid at home
how do you make Chenodeoxycholic Acid
Chenodeoxycholic Acid cas number
Chenodeoxycholic Acid burn symptoms
what is Chenodeoxycholic Acid found in
chemical formula Chenodeoxycholic Acid
what does Chenodeoxycholic Acid do
what is the formula of Chenodeoxycholic Acid
where is Chenodeoxycholic Acid found
molecular weight of Chenodeoxycholic Acid
Chenodeoxycholic Acid molecular formula
what is Chenodeoxycholic Acid formula
Chenodeoxycholic Acid Dosage
Take exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Do not take in larger or smaller amounts or for longer than recommended. Follow the directions on your prescription label.
chenodeoxycholic acid is usually taken 2 times each day until your gallstones are completely dissolved. Follow your doctor's instructions.
chenodeoxycholic acid is usually given for no longer than 2 years.
Use chenodeoxycholic acid regularly to get the most benefit. Get your prescription refilled before you run out of medicine completely.
It may take up to 12 months before your symptoms improve. Keep using the medication as directed and tell your doctor if your symptoms do not improve after 6 months of treatment.
To be sure this medication is not causing harmful effects, your liver function will need to be checked with frequent blood tests. You may also need an occasional ultrasound or x-ray examination of your gallbladder. Visit your doctor regularly.
chenodeoxycholic acid is only part of a complete program of treatment that may also include weight control and a special diet. It is very important to follow the diet plan created for you by your doctor or nutrition counselor. You should become very familiar with the list of foods you must avoid to help control your condition.
Even with treatment, there is a chance that your gallstones may return within 5 years. Talk to your doctor about your specific risk. Chenodiol will not prevent gallstones from occurring.
Store at room temperature away from moisture and heat. Keep the bottle tightly closed when not in use.
Seek emergency medical attention or call the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222.
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember. Skip the missed dose if it is almost time for your next scheduled dose. Do not take extra medicine to make up the missed dose.
Chenodeoxycholic acid Interactions
Follow your doctor's instructions about any restrictions on food, beverages, or activity. Avoid eating foods that are high in fat or cholesterol.
Tell your doctor about all other medicines you use, especially:
a blood thinner such as warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven);
cholestyramine (Prevalite, Questran) or colestipol (Colestid);
birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy; or
antacids that contain aluminum (such as Acid Gone, Aldroxicon, Alternagel, Di-Gel, Gaviscon, Gelusil, Maalox, Maldroxal, Mylagen, Mylanta, Rulox, and others).
This list is not complete and other drugs may interact with chenodiol. Tell your doctor about all medications you use. This includes prescription, over-the-counter, vitamin, and herbal products. Do not start a new medication without telling your doctor.
chenodeoxycholic acid [ke″no-de-ok″se-ko′lic]
one of the primary bile acids in humans, usually found conjugated with glycine or taurine; it facilitates fat absorption and cholesterol excretion. The pharmaceutical preparation, called chenodiol, is used in treatment of gallstones.
che·no·de·ox·y·cho·lic ac·id (kē'nō-dē-oks'ē-kō'lik as'id),
A major bile acid in many vertebrates, usually conjugated with glycine or taurine; it facilitates cholesterol excretion and fat absorption; administered to dissolve cholesterol gallstones.
chenodeoxycholic acid /che·no·de·oxy·cho·lic ac·id/ (ke″no-de-ok″se-kol′ik) a primary bile acid, usually conjugated with glycine or taurine; it facilitates fat absorption and cholesterol excretion.
chenodeoxycholic acid
[kē′nōdē·ok′sikō′lik]
a secondary bile acid. It is used in vivo to dissolve cholesterol gallstones, particularly in the elderly and poor-risk patients. See also ursodeoxycholic acid.
chenodeoxycholic acid A bile acid with detergent properties. It has been used as a drug to dissolve GALLSTONES, but this takes 6 months to 2 years.
che·no·de·ox·y·cho·lic ac·id (kē'nō-dē-oks'ē-kō'lik as'id)
A major bile acid in many vertebrates; facilitates cholesterol excretion and fat absorption; administered to dissolve cholesterol gallstones.
chenodeoxycholic acid
a primary bile acid, C24H40O4, administered as an anticholelithogenic agent. Called also chenodiol.
Ursodeoxycholic acid versus chenodeoxycholic acid
Chenodeoxycholic acid (cheno) and ursodeoxycholic acid (urso) dissolve cholesterol gallstones in man. In the present study the effects of cheno and urso were investigated in a prospective study in 10 patients in which every patient served as his own control. Five patients were first treated with cheno and subsequently with urso, and 5 patients were first treated with urso and subsequently with cheno. Each of the treatment periods lasted for 3 months. Cheno and urso were administered in daily doses of 12.7 to 17.9 mg per kg. In the control period biliary bile acids consisted of 40.7 ± 4.0% cheno, 1.4 ± 0.2% urso, 1.1 ± 0.1% lithocholic acid, and 0.7 ± 0.2% lithocholic acid sulfate. During treatment with cheno this bile acid increased in bile to 84.3 ± 1.6%, urso to 4.6 ± 1.2%, lithocholic acid to 2.0 ± 0.2%, and lithocholic acid sulfate increased to 1.6 ± 0.2%. In plasma cheno, lithocholic acid and lithocholic acid sulfate were increased. During treatment with urso this bile acid increased in bile to 57.1 ± 3.5% while cheno decreased to 17.9 ± 1.3%, lithocholic acid to 0.6 ± 0.1%, and lithocholic acid sulfate to 0.5 ± 0.1% of total biliary bile acids. In plasma only urso increased. Cholesterol saturation of bile decreased during both treatment periods but was significantly lower during urso treatment (0.6 ± 0.1) than during cheno treatment (0.8 ± 0.1). In 4 patients maximal SGPT values were elevated during the cheno treatment period in comparison to the control period and urso treatment period. All other liver function tests and also serum lipids were unchanged during both treatment periods.
Supramolecular Interactions of Chenodeoxycholic Acid Increase the Efficiency of Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells Based on a Cobalt Electrolyte
A combined experimental and computational study is carried out to understand the nature of the interfaces between dye-sensitized TiO2 and cobalt-based electrolyte in the presence of a prototype coabsorbent, chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA), employed in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSCs). It was recently reported that including CDCA both in the dye and in the electrolyte solutions substantially improved the performance of DSCs based on a Fc/Fc+ electrolyte (Daeneke et al. Nat. Chem.2011, 3, 1755) . Here, we evaluate the individual and combined effect of CDCA as a surface coadsorbent and as an additive in DSCs based on a Co(II)/Co(III) electrolyte, in combination with two prototypical Ru(II) dyes, N719 and Z907. For both dyes, the concomitant use of CDCA in the dye bath and in the electrolyte solution leads to a significant improvement, by about a factor of 2, of the DSCs photovoltaic performances, allowing us to reach 5.3% efficiency with Z907. FT-IR analyses conducted on the solid and TiO2-adsorbed CDCA highlight the presence of surface-adsorbed interacting CDCA molecules, possibly creating a bulky insulating network on the TiO2 surface. Computational analyses have been carried out to gain insight into the nature of the supramolecular aggregates occurring for CDCA on the TiO2 surface.


























































































| CasNo: | |
|---|---|
| *ProductName: | |
| *Num: | |
| *Purity: | |
| *Company: | |
| *Name: | |
| *Email: | |
| *Tel: | |
| * Requirements: | |
| Inquiry |
Address:A3 Building, Dongli Aviation Business District,No.8,Pingying Road, Dongli District, Tianjin, P.R.China, 300300 Tel:+86-022-58602231 Fax:+86-022-58602232 Email:nwsbio@163.com
Copyright © Tianjin NWS Biotechnology and Medicine Co. Ltd.